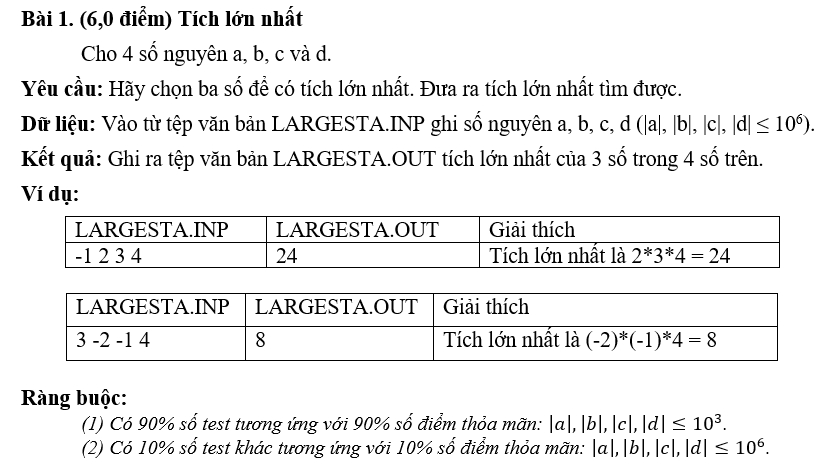
Đề thi học sinh giỏi môn Tin học
 Loading...
Loading...
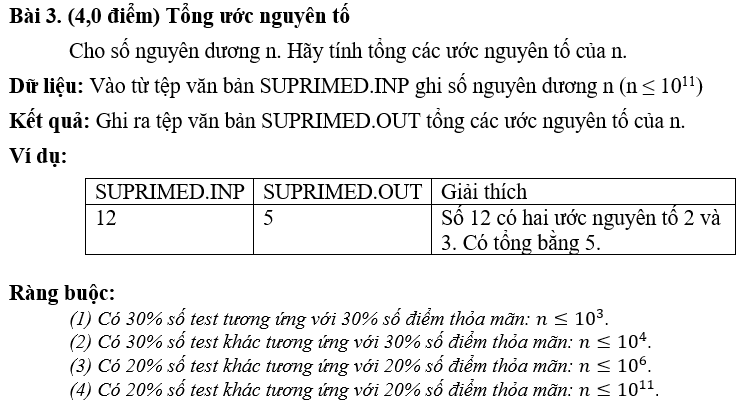
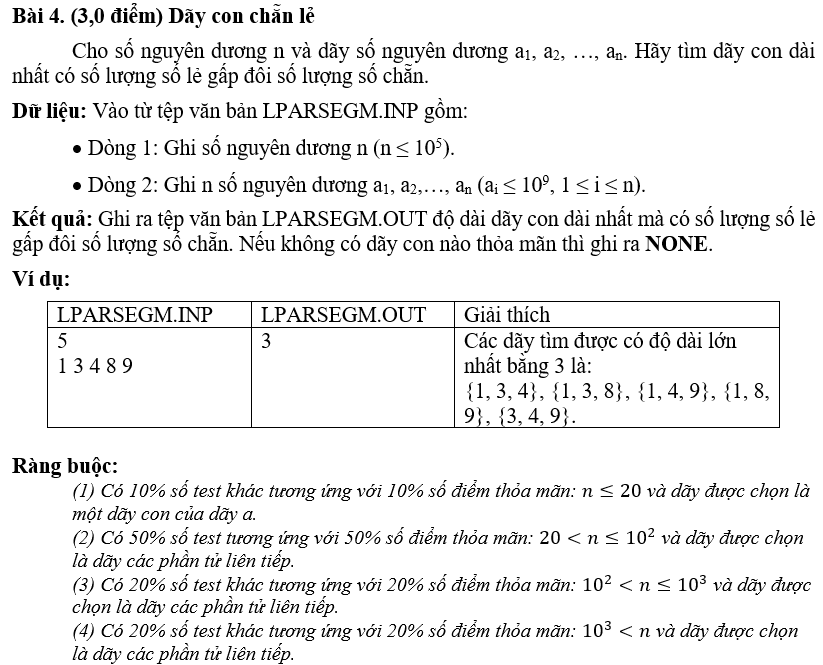
Hướng dẫn giải
Code C++:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a, b, c, d;
long long res1, res2, res3, res4, res;
int main()
{
freopen("LARGESTA.INP", "r", stdin);
freopen("LARGESTA.OUT", "w", stdout);
cin >> a >> b >> c >> d;
res1 = 1ll * a * b * c;
res2 = 1ll * a * b * d;
res3 = 1ll * a * c * d;
res4 = 1ll * b * c * d;
res = max(res1, max(res2,max(res3,res4)));
cout << res;
return 0;
}
Code Python:
# Đọc dữ liệu từ tệp vào
with open('LARGESTA.INP', 'r') as file_input:
a, b, c, d = map(int, file_input.readline().split())
# Tìm tổ hợp có tích lớn nhất
max_product = max(a * b * c, a * b * d, a * c * d, b * c * d)
# Ghi kết quả vào tệp ra
with open('LARGESTA.OUT', 'w') as file_output:
file_output.write(str(max_product))

Code C++:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define nmax 100007
using namespace std;
int a[nmax], n;
int res = 1e9; // Khởi tạo res bằng giá trị lớn
void findMinimumDifference() {
sort(a + 1, a + n + 1); // Sắp xếp mảng
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
res = min(res, abs(a[i] - a[i + 1])); // Cập nhật res với độ chênh lệch nhỏ nhất
}
}
int main() {
freopen("SMADIFFE.INP", "r", stdin);
freopen("SMADIFFE.OUT", "w", stdout);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
findMinimumDifference(); // Tìm độ chênh lệch nhỏ nhất
cout << res;
return 0;
}
Code Python:
# Đọc dữ liệu từ tệp vào
with open('SMADIFFE.INP', 'r') as file_input:
# Đọc số lượng phần tử N
N = int(file_input.readline().strip())
# Đọc dãy số nguyên a
a = list(map(int, file_input.readline().split()))
# Sắp xếp dãy số theo thứ tự tăng dần
a.sort()
# Tính độ chênh lệch nhỏ nhất giữa hai phần tử trong dãy
min_difference = float('inf')
for i in range(1, N):
difference = abs(a[i] - a[i - 1])
if difference < min_difference:
min_difference = difference
# Ghi kết quả vào tệp ra
with open('SMADIFFE.OUT', 'w') as file_output:
file_output.write(str(min_difference))
Code C++:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long n, tong, c[1000000], k = 0;
bool f[1000000];
void sangngto(long long n) //Sàng Eratosthenes
{
memset(f, true, sizeof(f));
f[1] = false;
int i = 2;
while((i * i) <= n)
{
if(f[i])
{
int k = 2;
while(i * k <= n)
{
f[i * k] = false;
k++;
}
i++;
}
else
i++;
}
}
void thuasont(long long N) //Phân tích N thành tích thừa số nguyên tố
{ // thu được mảng C có K phần tử kiểu long long (int64)
int i = 2;
while(i * i <= N)
{
if(N % i == 0)
{
c[++k] = i;
N /= i;
}
else
i++;
}
if(N > 1)
c[++k] = N;
}
void subtask3() //Cách 3
{
sangngto(n); //Sàng Eratosthenes tới N
for(int i = 1; i * i <= n; i++)
{
if(n % i == 0)
{
if(f[i])
tong += i;
if(i != n / i && f[n / i])
tong += n / i;
}
}
cout << tong;
}
void subtask4() //Cách 4
{
thuasont(n); //phân tích N thành tích các thừa số nguyên tố
tong = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= k; i++) //tính tổng các thừa số nguyên tố khác nhau
if(c[i] != c[i + 1])
tong += c[i];
cout << tong;
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
freopen("suprimed.inp","r",stdin);
freopen("suprimed.out","w",stdout);
cin >> n;
subtask4(); //gọi cách 4
return 0;
}
Code Python:
def sieve_of_eratosthenes(n):
prime = [True for _ in range(n+1)]
p = 2
while (p * p <= n):
if (prime[p] == True):
for i in range(p * p, n+1, p):
prime[i] = False
p += 1
return prime
def sum_of_prime_factors(n):
prime = sieve_of_eratosthenes(n)
sum_primes = 0
for i in range(2, n + 1):
if prime[i] and n % i == 0:
sum_primes += i
return sum_primes
def sum_of_unique_prime_factors(n):
prime_factors = []
i = 2
while i * i <= n:
if n % i == 0:
prime_factors.append(i)
while n % i == 0:
n //= i
i += 1
if n > 1:
prime_factors.append(n)
return sum(set(prime_factors))
# Đọc dữ liệu từ file
with open("suprimed.inp", "r") as file:
n = int(file.readline().strip())
# Tính tổng và ghi ra file
with open("suprimed.out", "w") as file:
sum_primes = sum_of_unique_prime_factors(n)
file.write(str(sum_primes))
Code C++:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 100005;
int main() {
freopen("LPARSEGM.INP", "r", stdin);
freopen("LPARSEGM.OUT", "w", stdout);
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int &x : a) cin >> x;
unordered_map<int, int> balance_index;
balance_index[0] = -1; // Khởi tạo với trường hợp cân bằng ban đầu
int odd_count = 0, even_count = 0, max_len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (a[i] % 2 == 0) even_count++;
else odd_count++;
int balance = odd_count - 2 * even_count;
if (balance_index.find(balance) == balance_index.end()) {
balance_index[balance] = i;
} else {
max_len = max(max_len, i - balance_index[balance]);
}
}
if (max_len == 0) cout << "NONE";
else cout << max_len;
return 0;
}
Code Python:
def find_longest_subarray(nums):
prefix_diff = 0
max_length = 0
last_seen = {0: -1}
odd_count = 0
even_count = 0
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
if num % 2 == 0:
even_count += 1
else:
odd_count += 1
prefix_diff = odd_count - 2 * even_count
if prefix_diff in last_seen:
max_length = max(max_length, i - last_seen[prefix_diff])
else:
last_seen[prefix_diff] = i
return max_length
with open("LPARSEGM.INP", "r") as f:
N = int(f.readline().strip())
numbers = list(map(int, f.readline().split()))
result = find_longest_subarray(numbers)
with open("LPARSEGM.OUT", "w") as f_out:
if result == 0:
f_out.write("NONE")
else:
f_out.write(str(result))

Code C++:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define nmax 100007
using namespace std;
int a[nmax], b[nmax];
long long n;
long long res = 0;
int k;
bool fre[nmax];
bool palin(long long u) {
string su = to_string(u);
string su0 = su;
reverse(su.begin(), su.end());
return (su0 == su);
}
void xuli() {
long long s = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
s = s * 10 + a[b[i]];
if (palin(s))
res = max(res, s);
}
void thu(int i) {
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++)
if (fre[j]) {
b[i] = j;
fre[j] = false;
if (i == k)
xuli();
else
thu(i + 1);
fre[j] = true;
}
}
void subtask3() {
memset(fre, true, sizeof(fre));
thu(1);
}
void phantich(long long u) {
k = 0;
while (u > 0) {
a[++k] = u % 10;
u /= 10;
}
}
int main() {
freopen("LSYMPERM.INP", "r", stdin);
freopen("LSYMPERM.OUT", "w", stdout);
cin >> n;
phantich(n);
subtask3();
cout << res;
return 0;
}
Code Python:
from collections import Counter
def create_largest_palindrome(N):
digit_count = Counter(str(N))
first_half = []
middle_digit = None
for digit, count in digit_count.items():
if count % 2 != 0:
if not middle_digit or digit > middle_digit:
middle_digit = digit
for digit, count in digit_count.items():
if digit == middle_digit:
count -= 1
first_half.extend([digit] * (count // 2))
first_half.sort(reverse=True)
if middle_digit:
return int(''.join(first_half) + middle_digit + ''.join(first_half[::-1]))
else:
return int(''.join(first_half) + ''.join(first_half[::-1]))
# Đọc dữ liệu từ file LSYMPERM.INP
with open('LSYMPERM.INP', 'r') as file:
N = int(file.read().strip())
# Tạo số đối xứng lớn nhất
largest_palindrome = create_largest_palindrome(N)
# Ghi kết quả vào file LSYMPERM.OUT
with open('LSYMPERM.OUT', 'w') as file:
file.write(str(largest_palindrome))

